 with
cardinality
with
cardinality 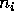 , with
, with 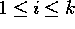 . Then the following indices are
defined [4,12,28,29]
setting
. Then the following indices are
defined [4,12,28,29]
setting 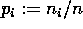 :
:
The idea of the topological information indices is to apply the
general formula for information entropy by Shannon
[26,27]
to chemical graphs. For that purpose, an equivalence relation is
defined partitioning the n vertices of a graph
in k disjoint sets  with
cardinality
with
cardinality 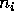 , with
, with 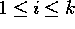 . Then the following indices are
defined [4,12,28,29]
setting
. Then the following indices are
defined [4,12,28,29]
setting 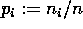 :
:
SIC is stands for structural information content, while CIC means complementary information content. These can be computed for different underlying equivalence relations. In this paper, we only consider the first order neighborhood [12,29]. Here two vertices of the molecular graph (including hydrogens) are considered equivalent iff they have equal atom types, and for each neighbor of the first vertex there exists a neighbor of the second one of the same type and the same connectivity to the atom in question.